How to operate a drone safely and effectively is crucial for both recreational and professional users. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding regulations and safety protocols to mastering flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial photography. We’ll cover everything from pre-flight checks and calibration to troubleshooting common issues, ensuring you’re well-equipped to confidently take to the skies.
We will explore the essential components of a drone, explain the various flight modes, and provide practical tips for achieving smooth, stable footage. Whether you’re a novice pilot or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will empower you to unlock the full potential of your drone.
Drone Regulations and Safety
Operating a drone responsibly requires understanding and adhering to local regulations and prioritizing safety. This section details essential safety procedures, licensing requirements, and regulatory comparisons across different countries.
Drone Licensing and Certification Requirements
Drone regulations vary significantly worldwide. Many countries categorize drones based on weight and intended use, leading to different licensing requirements. For example, in the United States, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) requires registration for most drones and may necessitate a Remote Pilot Certificate for commercial operations. Similarly, in the European Union, drone operators often need to register their drones and obtain specific certifications based on the drone’s class and intended use.
In some countries, licensing may be less stringent for recreational use but still requires adherence to specific airspace rules. Always check the specific regulations in your country or region before flying.
Drone Safety Procedures
Safe drone operation involves a multi-stage process encompassing pre-flight checks, in-flight awareness, and post-flight procedures.
- Pre-flight: Thoroughly inspect the drone for any damage, ensure sufficient battery charge, check weather conditions (avoid strong winds or rain), and verify airspace restrictions via apps like AirMap or B4UFLY.
- In-flight: Maintain visual line of sight with the drone, avoid flying near people or obstacles, and be mindful of airspace restrictions. Respect privacy and never fly over private property without permission.
- Post-flight: Safely land the drone, power it down, and inspect it for any damage. Store the drone and its components properly to protect them from damage.
Drone Pre-Flight Inspection Checklist

A comprehensive pre-flight checklist ensures a safe and successful flight.
- Inspect drone body for damage
- Check propeller condition
- Verify battery charge and health
- Inspect camera and gimbal
- Check GPS signal strength
- Review weather conditions
- Confirm airspace authorization
Safety Briefing for New Drone Pilots
A thorough safety briefing should be given to all new drone pilots before their first flight. This briefing should cover the basics of safe drone operation, including pre-flight checks, emergency procedures, and the importance of adhering to local regulations.
Drone Regulations Comparison
This table compares drone regulations across three countries (these are simplified examples and may not be fully comprehensive; always refer to official sources):
| Country | Registration Required | Licensing Requirements (Commercial) | Airspace Restrictions |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Generally Yes (for most drones) | FAA Part 107 Remote Pilot Certificate | Vary by location; use apps like B4UFLY |
| United Kingdom | Yes (for most drones) | Operational Authorisation depending on drone class and operation | Controlled airspace restrictions apply |
| Canada | Yes (for most drones) | Basic and Advanced certificates available through Transport Canada | Restricted airspace near airports and other sensitive areas |
Understanding Drone Components and Controls
Understanding your drone’s components and how to control it is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section covers key components, controller types, connection procedures, sensor calibration, and troubleshooting common malfunctions.
Key Drone Components and Their Functions
A typical drone consists of several key components:
- Frame: The main structure supporting all other components.
- Motors: Provide the power for propulsion.
- Propellers: Generate thrust for flight.
- Electronic Speed Controllers (ESCs): Control the speed of each motor.
- Flight Controller: The “brain” of the drone, responsible for stabilizing flight and processing sensor data.
- GPS Module: Provides location data for autonomous flight.
- Battery: Provides power to the drone.
- Camera (optional): Captures photos and videos.
- Gimbal (optional): Stabilizes the camera for smoother footage.
Drone Controllers and Functionalities
Drone controllers vary in features and complexity. Many offer adjustable settings for responsiveness, control modes, and other parameters. Some controllers include built-in displays, while others rely on a smartphone or tablet for feedback.
Connecting a Drone to its Controller, How to operate a drone

The process of connecting a drone to its controller varies slightly depending on the specific model. Generally, it involves turning on the drone and controller, then pairing them via a specific button sequence or software application. Consult your drone’s user manual for precise instructions.
Drone Sensor Calibration Techniques
Proper sensor calibration is essential for accurate and stable flight. This typically involves placing the drone on a level surface and following the instructions provided in the drone’s user manual or the controller’s software.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Here’s a list of common drone malfunctions and their possible troubleshooting steps:
- GPS Signal Loss: Check for obstructions, ensure sufficient satellites are acquired, and try restarting the drone.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery or use a spare battery.
- Motor Malfunctions: Inspect motors and propellers for damage. If problems persist, seek professional assistance.
- Gimbal Issues: Check gimbal calibration and ensure proper tightening.
- Communication Issues: Ensure proper controller connection and check for interference.
Pre-Flight Preparations and Procedures
Meticulous pre-flight preparation is crucial for safe and successful drone operation. This section details planning a safe flight, choosing appropriate flight modes, performing pre-flight checks, and preparing the drone’s battery.
Planning a Safe Drone Flight
Planning involves checking weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation), verifying airspace restrictions using online tools or apps, and identifying potential hazards in the flight area. Ensure you have sufficient battery life for the planned flight duration.
Choosing Appropriate Flight Modes
Different flight modes cater to various scenarios. GPS mode provides stability and location awareness, while Attitude mode allows for more agile maneuvers. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of each mode is crucial for safe operation.
Pre-Flight Calibration and System Check
Before each flight, calibrate the drone’s sensors (IMU, compass) and perform a thorough system check, including verifying motor function, GPS signal strength, and camera operation. This ensures the drone is ready for a safe flight.
Pre-Flight Checklist Flowchart
A visual flowchart effectively guides pre-flight checks. The flowchart would begin with “Power On Drone & Controller,” followed by steps such as “Check Battery Level,” “Check Propellers,” “Calibrate IMU,” “Check GPS Signal,” “Check Airspace,” and finally, “Ready for Takeoff.”
Drone Battery and Charging Equipment Checklist
Proper battery management is vital. The checklist would include verifying battery charge levels, ensuring proper charging methods, and having spare batteries readily available. Inspect the charging equipment for any damage.
Drone Flight Techniques and Maneuvers
Mastering basic flight controls and maneuvers is fundamental to safe and effective drone piloting. This section covers basic controls, flight modes, and common maneuvers.
Basic Flight Controls
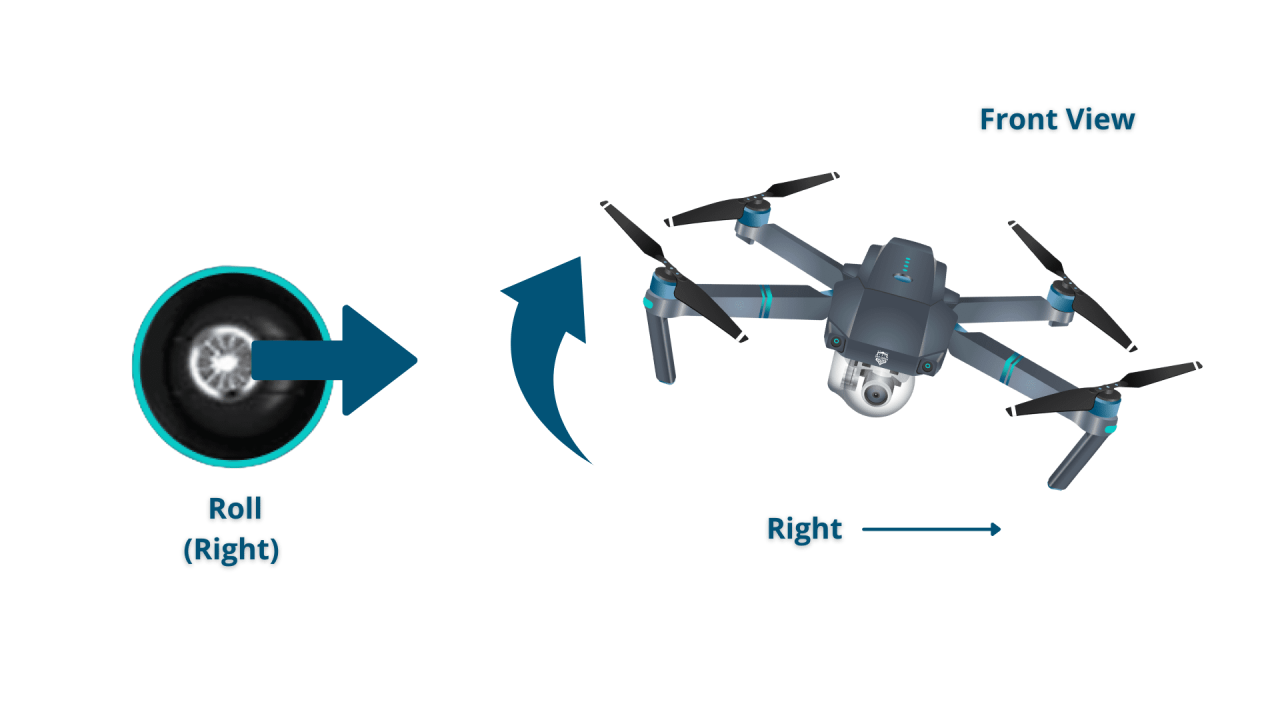
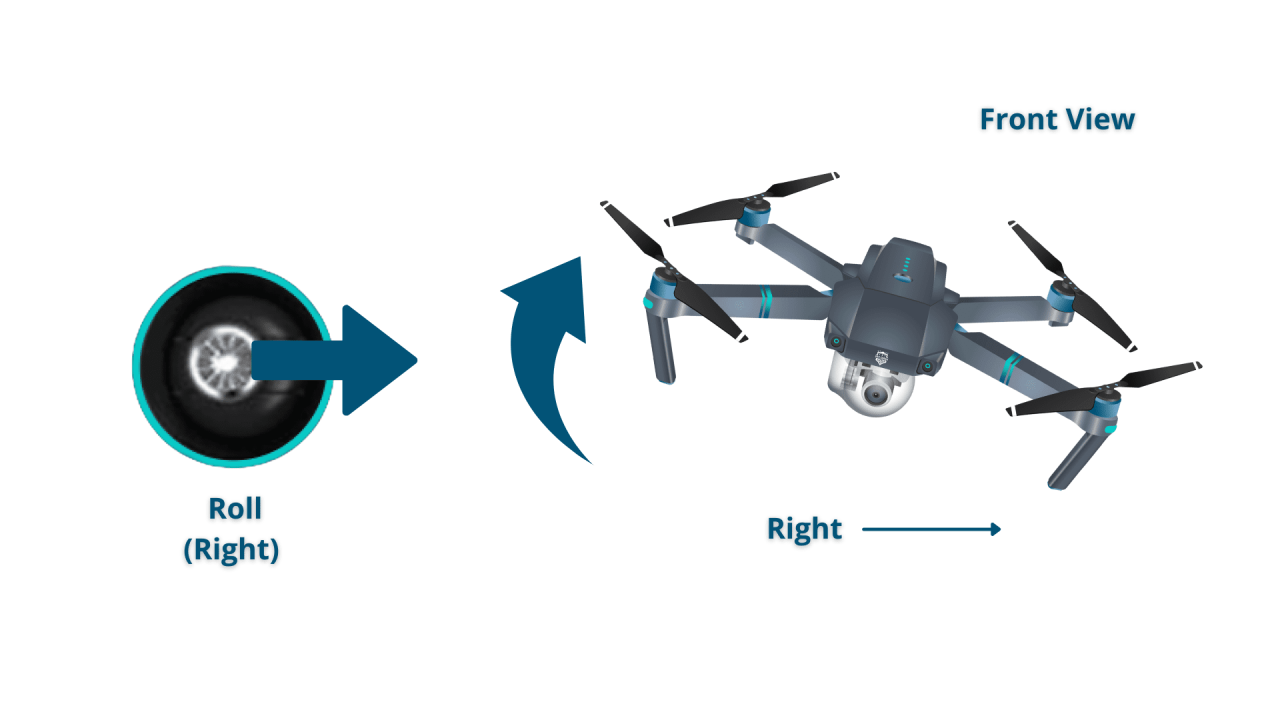
The basic controls are throttle (altitude), pitch (forward/backward), roll (left/right), and yaw (rotation). Understanding how these controls interact is key to precise maneuvering.
Different Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of stability and control. GPS mode relies on satellite data for stable flight, while Attitude mode provides more responsiveness but requires more pilot skill.
Basic Drone Maneuvers
Basic maneuvers include taking off, landing, hovering, and moving in different directions. Practice these maneuvers in a safe, open area to develop proficiency.
Comparison of Flight Styles
Different flight styles are suitable for various purposes. Smooth, slow movements are ideal for photography and videography, while more agile maneuvers might be needed for inspections or racing.
Common Drone Maneuvers and Control Inputs
| Maneuver | Throttle | Pitch | Roll | Yaw |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Takeoff | Increase | Neutral | Neutral | Neutral |
| Hover | Maintain | Neutral | Neutral | Neutral |
| Forward | Maintain | Forward | Neutral | Neutral |
| Turn Left | Maintain | Neutral | Neutral | Left |
Drone Photography and Videography
Capturing high-quality photos and videos with a drone requires understanding camera settings, composition techniques, and stabilization methods. This section provides guidance on achieving optimal image and video quality.
Adjusting Drone Camera Settings
Adjusting settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture affects image quality. Experiment with these settings to find the optimal balance for different lighting conditions.
Techniques for Composing Shots
Effective composition involves choosing interesting angles, using leading lines, and considering the rule of thirds. Experiment with different perspectives to capture unique shots.
Achieving Smooth and Stable Footage
Smooth footage requires stable flight and potentially the use of a gimbal. Practice smooth movements and avoid jerky transitions.
Using Different Camera Modes
Different camera modes like photo, video, and timelapse offer various creative possibilities. Understanding each mode’s capabilities is essential for effective use.
Planning and Executing a Drone Photography Project
Planning involves selecting the location, considering lighting conditions, and defining the desired shots. Execute the plan methodically, ensuring safety and capturing high-quality content.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance ensure the longevity and safe operation of your drone. This section details safe landing, inspection, maintenance tasks, and storage tips.
Safely Landing and Securing the Drone
Always land the drone in a safe, open area, away from obstacles and people. Power down the drone and secure it to prevent damage or theft.
Regular Drone Inspection and Maintenance
Regular inspections identify potential issues early. Check for damage to the frame, propellers, and other components.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is available at how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to safe landing procedures. Mastering these techniques ensures responsible and enjoyable drone operation.
Common Maintenance Tasks and Frequency
Tasks include cleaning the drone, lubricating moving parts, and checking for loose screws or connections. The frequency depends on usage but should be done at least after every few flights.
Proper Storage of Drone and Accessories
Store the drone and accessories in a clean, dry, and safe place to protect them from damage.
Recommended Drone Maintenance Schedule
| Task | Frequency | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | After each flight | Check for damage or loose parts |
| Cleaning | After each flight | Remove dirt and debris |
| Battery Check | Before each flight | Ensure sufficient charge |
| Propeller Check | Before each flight | Check for damage or wear |
Troubleshooting Common Drone Issues: How To Operate A Drone
This section addresses common drone problems, troubleshooting steps, error message interpretation, and preventative strategies.
Common Drone Problems and Troubleshooting Steps
Common problems include GPS signal loss, low battery, motor malfunctions, and communication issues. Troubleshooting involves systematically checking each component and its connections.
Interpreting Drone Error Messages
Understanding error messages helps in diagnosing problems. Consult the drone’s manual for explanations of specific error codes.
Strategies for Preventing Common Drone Malfunctions
Preventive measures include regular maintenance, proper storage, and avoiding extreme weather conditions.
Troubleshooting Guide
- No Power: Check battery connection and charge level.
- Motor Failure: Inspect motors and propellers for damage.
- GPS Issues: Check for obstructions and restart the drone.
- Camera Malfunction: Check camera settings and connections.
Mastering drone operation is a journey that combines theoretical knowledge with practical experience. By understanding drone regulations, mastering flight controls, and implementing proper maintenance procedures, you can safely and confidently explore the world from a unique perspective. Remember that continuous learning and practice are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. Embrace the challenges, enjoy the flight, and capture breathtaking moments from above.
FAQs
What type of drone is best for beginners?
For beginners, a user-friendly drone with GPS stabilization, autonomous return-to-home features, and a relatively simple control interface is recommended. Many models offer these features at a reasonable price point.
How long does a drone battery typically last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, size, and flight conditions. Expect flight times ranging from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge, but always check your specific drone’s specifications.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is a comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and efficient drone operation, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable and productive experience.
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately switch to a lower flight mode (if available), attempt to regain signal, and prepare for a controlled landing. Consult your drone’s manual for specific instructions.
How often should I calibrate my drone?
Calibrating your drone’s sensors should be done before each flight session to ensure optimal performance and accuracy. Consult your drone’s manual for the specific calibration procedure.
Where can I find information on local drone regulations?
Check your country’s and local civil aviation authority websites for up-to-date drone regulations and airspace restrictions. These regulations often vary by location.